2.1 Abstracting physical resources
2.2 User mode, supervisor mode, and system calls
2.3 Kernel Organization
monolithic kernel vs microkernel
xv6 和 Unix-like OS 属于 monolithic kernel.
2.4 Code: xv6 organization
kernel 接口都在 def.h 中声明.
2.5 Process overview
进程的地址空间:
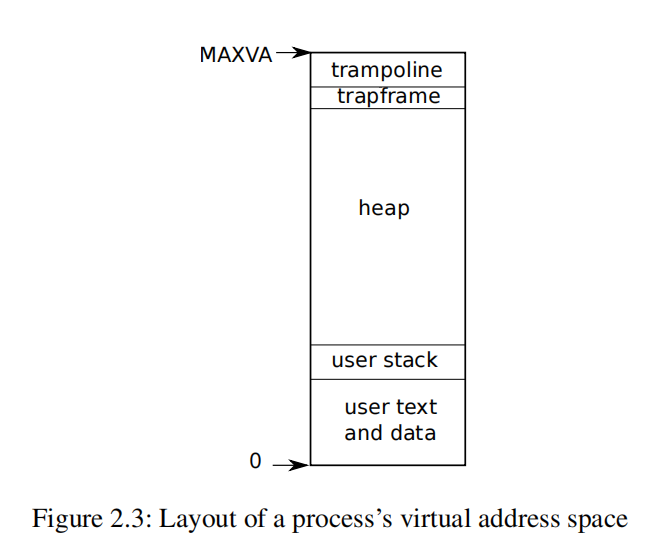
RISC-V 64 只使用 64 位地址中的 39 位, 所以用户空间和内核空间各占 2^39 字节.
xv6 只使用 39 位地址中的 38 位, 所以最大地址为 2^38 - 1 = 0x3fffffffff, MAXVA 在 riscv.h 中定义.
每个进程都有两个栈, 一个是内核栈, 一个是用户栈.
2.6 Code: starting xv6, the first process and system call
bootloader 把 xv6 kernel code 加载到内存 0x80000000 地址, 首先执行的代码为entry.S 的 _entry函数. 为每个 CPU 设置堆栈指针 sp,然后跳进start.c的 start 函数。
# qemu -kernel loads the kernel at 0x80000000
# and causes each CPU to jump there.
# kernel.ld causes the following code to
# be placed at 0x80000000.
.section .text
.global _entry
_entry:
# set up a stack for C.
# stack0 is declared in start.c,
# with a 4096-byte stack per CPU.
# sp = stack0 + (hartid * 4096)
la sp, stack0 # 先设置sp为stack0的起始地址
li a0, 1024*4
csrr a1, mhartid # CPUs 0~7 has hartid from 0~7, 获取当前CPU的hartid
addi a1, a1, 1 # 这边要加1的原因是栈地址从高到低
mul a0, a0, a1
add sp, sp, a0
# jump to start() in start.c
call start
spin:
j spin
stack0 在start.c中定义, __attribute__ ((aligned (16))) char stack0[4096 * NCPU];, 8 个 CPU, 共 4096*8 字节的大小.
根据上面的汇编代码, hardid=0 的话, sp 指针地址为 stack0 + 4096, 从高地址到低地址存放.
start.c 设置 mstatus 寄存器, 设置之前的 mode 为 supervisor mode, 这样最后调用mret, 可以从 machine mode 进入 supervisor mode, 并跳转至mepc中存入的 main 函数地址。
void start()
{
unsigned long x = r_mstatus();
x &= ~MSTATUS_MPP_MASK;
x |= MSTATUS_MPP_S;
w_mstatus(x);
w_mepc((uint64)main);
// ...
asm volatile("mret");
}
main.c userinit()中创建第一个进程。
void main()
{
// ...
userinit();
}
userinit.c uvminit把uchar initcode[] 即user/initcode.S编译出来的initcode可执行程序加载进进程的页表中。
void userinit(void)
{
struct proc *p;
p = allocproc();
uvminit(p->pagetable, initcode, sizeof(initcode));
}
接着initcode会执行系统调用exec执行/init用户程序。
initcode.S
# exec(init, argv)
.globl start
start:
la a0, init
la a1, argv
li a7, SYS_exec
ecall
最终在init.c中调用fork()在子进程中执行 shell 进程exec("sh", argv);,父进程则进入死循环。
4.3 Code: Calling system calls
initcode.S 把执行exec的参数存放在a0,a1寄存器中, 把 system call 编号存在a7寄存器中。随后ecall指令会 trap into kernel, 导致进入uservec和usertrap函数, 最后调用到sys_exec函数。
4.4 Code: System call arguments
User space 通过系统调用进入 kernel space, 参数保存在 current process 当前进程的 trap frame 中。
比如exit(0), 0 会被保存到a0寄存器,随后会被 kernel 保存到p->trapframe->a0。
argint, argaddr, argfd函数从当前进程的 trap frame 中读取传入的参数。
如果 user space 传入指针,会有两个问题。
- user space 可能传入 invalid address 或者是企图访问 kernel memory 的恶意指针。
- xv6 kernel page table 和 user space 的 page table mapping 不同,所以同一个虚拟地址对应的物理地址是不同的。
这时候需要用copyinstr函数。