CSRs
参考riscv-privileged-20211203.pdf
sstatus
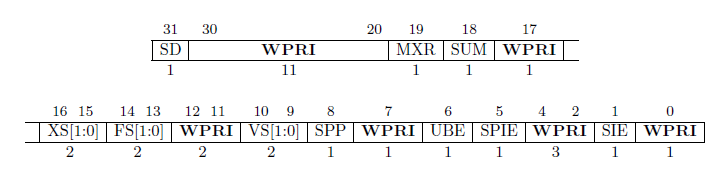
SPP: 在进入S mode之前hart处于什么mode。 用户态trap进入S mode,SPP被设置为0,其他情况为1。 如果SPP为0,执行SRET后,返回U mode。如果SPP为1,执行SRET后,返回S mode。随后SPP置0。
SIE: 1开启/0关闭 S mode的所有中断 in S mode。 在U mode时,SIE被忽略,S mode 的中断都是打开的。
SPIE: 当trap进入S mode,SIE会置0禁止S mode所有中断,SIE的旧值会保存到SPIE中。 执行SRET后,SIE被设置为SPIE中之前保存的旧值,SPIE置1。
stvec
Supervisor Trap Vector Base Address Register, 保存S mode异常/中断的跳转地址。


MODE为0,直接跳转到BASE;MODE为1,跳转到BASE + cause * 4。
在linux entry.S中的做法为直接设置stvec为handle_exception地址,地址的后两位肯定是4bytes对齐的,所以为00。跳转到handle_exception后,分开处理中断、系统调用、异常。根据异常cause再跳转到不同的异常处理函数。
SIP SIE
Supervisor Interrupt pending/enable Registers
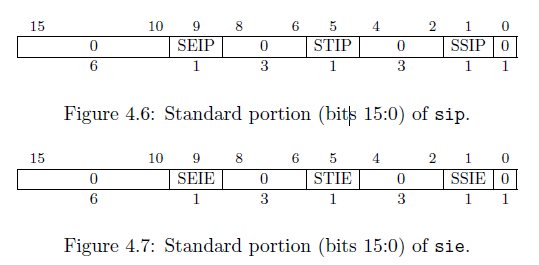
- SIP中断挂起(待处理的中断)和SIE中断使能。每一位代表的中断与scause中的为每个中断分配的异常码一致。
- 当sstatus.SIE=1, SIP[x]=1, SIE[x]=1,表示系统能够处理某个中断。
- SIP中有的位是只读的,不能通过直接写0来清除:
- SEIP is read-only in sip, and is set and cleared by the execution environment, typically through a platform-specific interrupt controller.
- STIP is read-only in sip, and is set and cleared by the execution environment.
- SSIP is writable in sip and may also be set to 1 by a platform-specific interrupt controller.
- 看系统中实现了哪些interrupts,可以直接通过写SIE某位为1来enable,再读回SIE看是否为1,来判断是否实现了。
- sip,sie的bit 3,7,11分别代表了M mode的software,timer,external interrupts,因为大多数平台不会将M mode的中断委托到S mode,所以图4.6和4.7中相应的位直接为0了。
- 优先级:SEI>SSI>STI。
scounteren
sscratch
sepc
Supervisor Exception Program Counter.
当trap发生时,sepc保存发生中断/异常指令的虚拟地址。
如果需要返回到sepc后一条指令,就需要在sret之前修改sepc的值。
对于同步异常,sepc指向导致异常的指令;对于中断,它指向中断处理后应该恢复执行的位置。
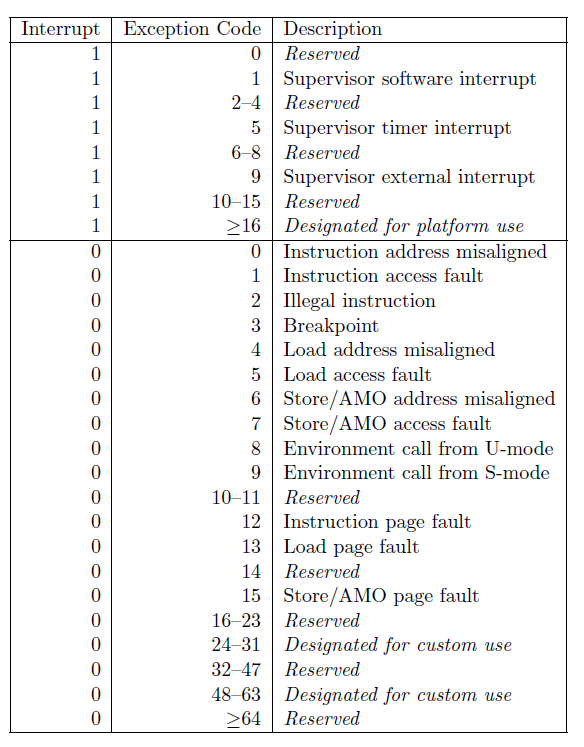
scause
保存发生中断/异常指令的事件。

stval
kernel中/ptrace.h pt_regs中的badaddr就是stval。发生kernel panic会打印出badaddr(stval)。
当instruction fetch/load/store时发生breakpoint(3), address-misaligned, access-fault, page-fault,stval会保存导致错误的虚拟地址。
当发生不对齐load/store导致的access-fault/page-fault, stval包含导致故障访问的虚拟地址。
当发生instruction access-fault(1) or page-fault(12),stval保存导致故障的指令的虚拟地址,此时sepc也会指向指令的开始地址。
illegal instruction(2), spec71页。
其他trap,还没实现,stval的值都为0。