Introduction to devicetree
All Zephyr and application source code files can include and use devicetree.h. This includes device drivers, applications, tests, the kernel, etc.
i2c从设备的reg地址是i2c slave address.
spi从设备的reg地址是chip select.
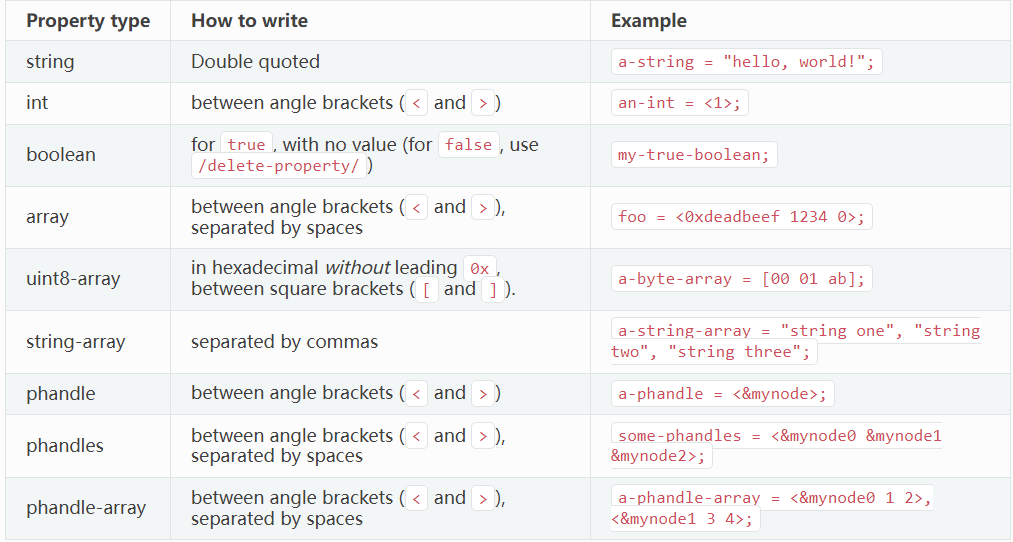
Writing property values

devicetree_unfixed.h, devicetree_fixups.h: deivcetree编译出来的一些宏供C使用。
zephyr3.5只有devicetree_generated.h
Devicetree bindings
Binding文件用来规范设备树每个节点的表达。
The build system uses bindings to generate C macros for devicetree properties that appear in DTS files. 如果binding文件中没有列出来,不会生成C宏。
# A high level description of the device the binding applies to:
description: |
This is the Vendomatic company's foo-device.
Descriptions which span multiple lines (like this) are OK,
and are encouraged for complex bindings.
See https://yaml-multiline.info/ for formatting help.
# You can include definitions from other bindings using this syntax:
include: other.yaml
# Used to match nodes to this binding:
compatible: "manufacturer,foo-device"
properties:
# Requirements for and descriptions of the properties that this
# binding's nodes need to satisfy go here.
child-binding:
# You can constrain the children of the nodes matching this binding
# using this key.
# If the node describes bus hardware, like an SPI bus controller
# on an SoC, use 'bus:' to say which one, like this:
bus: spi
# If the node instead appears as a device on a bus, like an external
# SPI memory chip, use 'on-bus:' to say what type of bus, like this.
# Like 'compatible', this key also influences the way nodes match
# bindings.
on-bus: spi
foo-cells:
# "Specifier" cell names for the 'foo' domain go here; example 'foo'
# values are 'gpio', 'pwm', and 'dma'. See below for more information.
<property name>:
required: <true | false>
type: <string | int | boolean | array | uint8-array | string-array |
phandle | phandles | phandle-array | path | compound>
deprecated: <true | false>
default: <default>
description: <description of the property>
enum:
- <item1>
- <item2>
...
- <itemN>
const: <string | int | array | uint8-array | string-array>
specifier-space: <space-name>
- required: true表示必须要这个属性。
- deprecated: true表示如果有这个属性,编译会出现warning。
- default: 如果dts没有某个属性,会提供一个默认值给该属性。与required:true不能同时出现。
- enum: 提供value的可选范围。
- const: 提供value必须选择的值。
Devicetree access from C/C++
Node identifiers
get a node identifier:
数字字母全部小写,非数字和字母的全部转化为下划线。
By path:DT_PATH(...): 输入根节点后的node路径,返回node identifier。如:DT_PATH(soc, serial_40001000, ...)。
By node label:DT_NODELABEL(label): 输入label名称。如:DT_NODELABEL(serial1)
By alias:DT_ALIAS(alias): 输入/aliases下的node。
By instance number:DT_INST(inst, compat): 根据指定的inst number和compat来找node。注意:compat相同的nodes中,status为disabled的inst number接在其他number后面。其他的inst number顺序不确定。
By chosen node:DT_CHOSEN(prop): 输入/chosen下的node。
By parent/child:DT_PARENT(), DT_CHILD()
DT_COMPAT_GET_ANY_STATUS_OKAY(compat) 根据compatible找到任意status为ok的对应节点。
e.g.
/dts-v1/;
/ {
aliases {
sensor-controller = &i2c1;
};
soc {
i2c1: i2c@40002000 {
compatible = "vnd,soc-i2c";
label = "I2C_1";
reg = <0x40002000 0x1000>;
status = "okay";
clock-frequency = <100000>;
};
};
};
以下几种方法都可以找到i2c@40002000node。
DT_PATH(soc, i2c_40002000)DT_NODELABEL(i2c1)DT_ALIAS(sensor_controller)DT_INST(x, vnd_soc_i2c)for some unknown number x.
Property access
Simple properties
DT_NODE_HAS_PROP(node_id, prop): 检查node_id是否有prop属性。DT_PROP(node_id, prop): 返回node_id的prop属性。本质是拼接node_id和prop,再到devicetree_generated.h中找宏。DT_PROP_LEN(node_id, prop): 获取prop的长度。DT_PROP_XXX不能用于reg和interrupts prop。
reg properties
reg prop需要使用:DT_REG_ADDR(node_id): return address。DT_REG_SIZE(node_id): return size。
如果有多个reg blocks: 注意idx只能传入数字或宏,不能在循环中传入i。DT_REG_ADDR_BY_IDX(node_id, idx)DT_REG_SIZE_BY_IDX(node_id, idx)
interrupt properties
interrupts prop需要使用:DT_NUM_IRQS(node_id): 返回interrupts prop中有多少个value。比如interrupts = <33, 1>。会return 2。第一个表示中断号,第二个是中断优先级。
DT_IRQ_BY_IDX():
...
#interrupt-cells = <2>
...
my-serial: serial@abcd1234 {
interrupts = < 33 0 >, < 34 1 >;
};
#define SERIAL DT_NODELABEL(my_serial)
Example usage Value
------------- -----
DT_IRQ_BY_IDX(SERIAL, 0, irq) 33
DT_IRQ_BY_IDX(SERIAL, 0, priority) 0
DT_IRQ_BY_IDX(SERIAL, 1, irq, 34
DT_IRQ_BY_IDX(SERIAL, 1, priority) 1
phandle properties
convert a phandle to a node identifier:DT_PHANDLE()DT_PHANDLE_IDX()DT_PHANDLE_BY_NAME()
convert the devicetree-level phandle to a Zephyr driver-level struct device:
方法1:DEVICE_DT_GET()必须要跟device_is_ready来检查。
#define MY_SERIAL DT_NODELABEL(serial0)
const struct device *const uart_dev = DEVICE_DT_GET(MY_SERIAL);
if (!device_is_ready(uart_dev)) {
/* Not ready, do not use */
return -ENODEV;
}
方法2:device_get_binding()
const char *dev_name = "UART_0";
const struct device *uart_dev = device_get_binding(dev_name);
access specifier values in a phandle array:DT_PHA_BY_IDX()DT_PHA()
Other APIs
Device driver conveniences
#include <zephyr/devicetree.h>
#define DT_DRV_COMPAT my_driver_compat
/* This is same thing as DT_INST(0, my_driver_compat): */
DT_DRV_INST(0)
/*
* This is the same thing as
* DT_PROP(DT_INST(0, my_driver_compat), clock_frequency)
*/
DT_INST_PROP(0, clock_frequency)
The /zephyr, user mode
/zephyr, user 节点可以不用写binding文件,直接提供给user space使用。