Book Notes
The Decorator Pattern: attaches additional responsibilities to an object dynamically. Decorators provide a flexible alternative to subclassing for extending functionality.
- Decorators have the same supertype as the objects they decorate.
- You can use one or more decorators to wrap an object.
- The decorator adds its own behavior before and/or after delegating to the object it decorates to do the rest of the job.
Design Pattern:
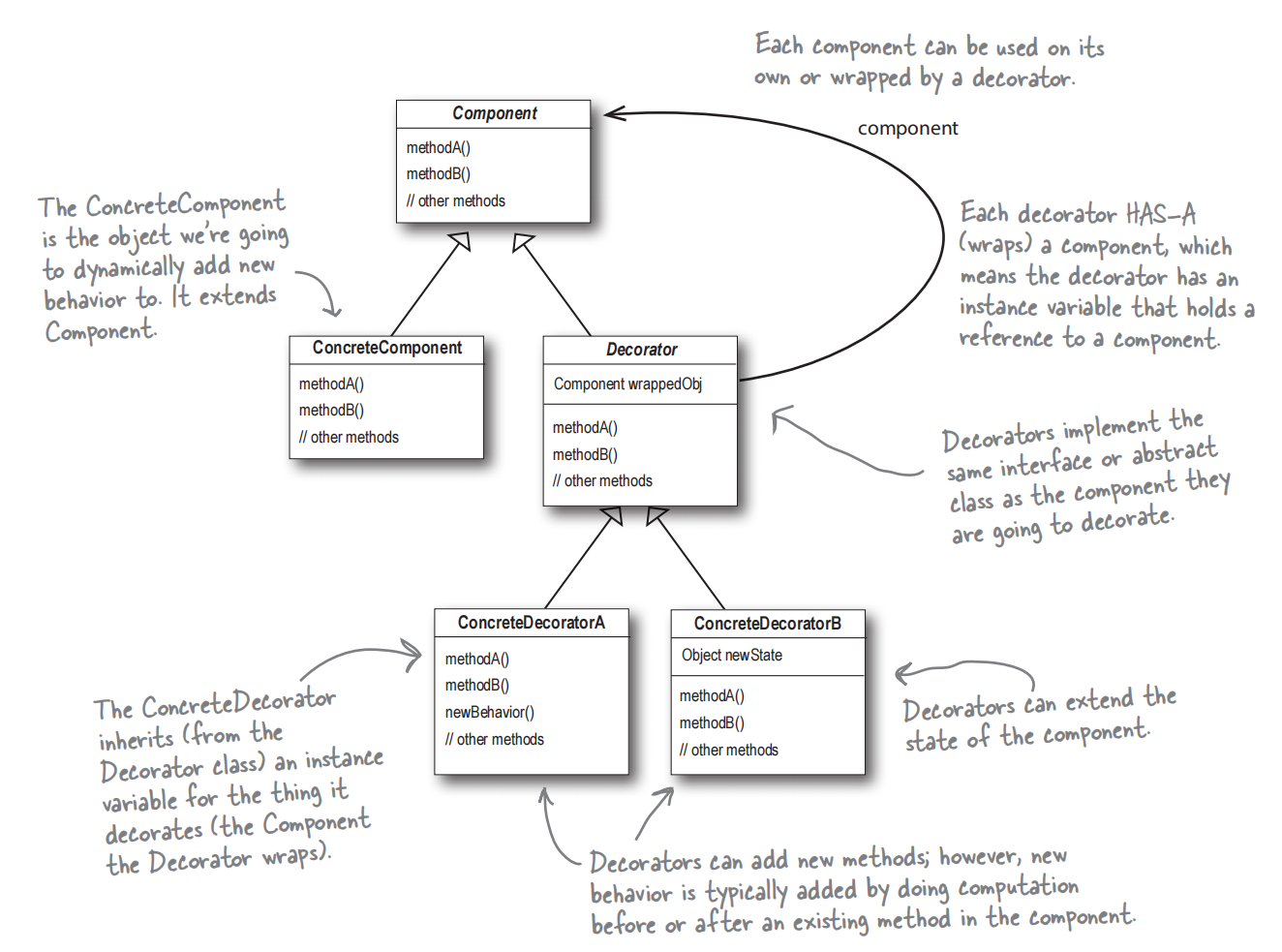
Example
咖啡店饮品案例:
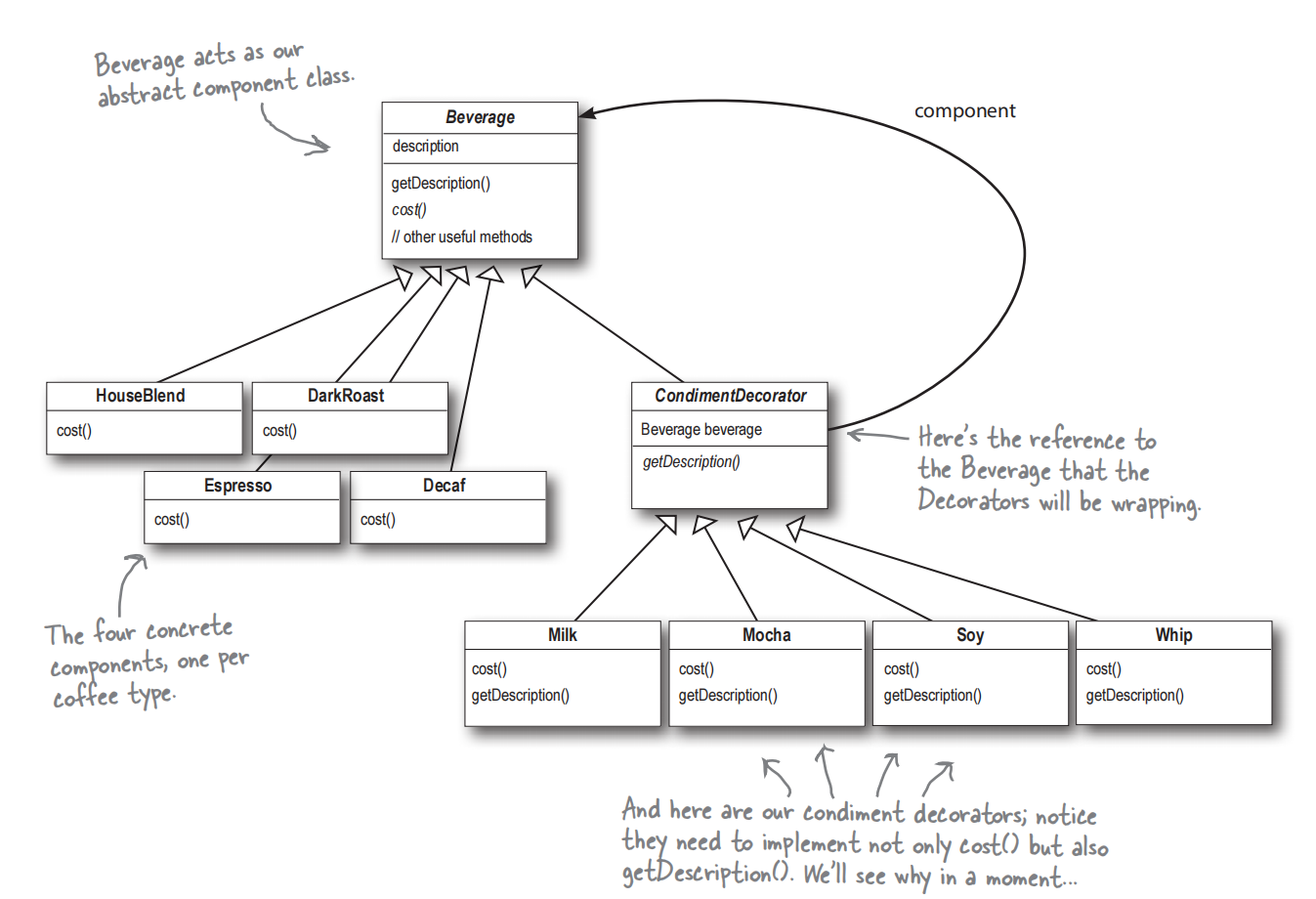
Beverage 和 CondimentDecorator 是两个抽象类,Beverage 是基类,CondimentDecorator 是装饰者基类:
public abstract class Beverage {
String description = "Unknown Beverage";
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public abstract double cost();
}
public abstract class CondimentDecorator extends Beverage {
Beverage beverage;
public abstract String getDescription();
}
DarkRoast 和 Espresso 是具体的饮料类:
public class DarkRoast extends Beverage {
public DarkRoast() {
description = "Dark Roast Coffee";
}
public double cost() {
return .99;
}
}
public class Espresso extends Beverage {
public Espresso() {
description = "Espresso";
}
public double cost() {
return 1.99;
}
}
Milk 和 Mocha 是具体的装饰者类:
public class Milk extends CondimentDecorator {
public Milk(Beverage beverage) { // 装饰者类需要接收一个饮料对象作为参数
this.beverage = beverage;
}
public String getDescription() { // 装饰者类需要实现和父类一样的 getDescription 方法
return beverage.getDescription() + ", Milk";
}
public double cost() { // 装饰者类需要实现和父类一样的 cost 方法
return .10 + beverage.cost();
}
}
public class Mocha extends CondimentDecorator {
public Mocha(Beverage beverage) {
this.beverage = beverage;
}
public String getDescription() {
return beverage.getDescription() + ", Mocha";
}
public double cost() {
return .20 + beverage.cost();
}
}
test code:
装饰类可以无限嵌套,并且和父类有一样的类型。
public class StarbuzzCoffee {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Beverage beverage = new Espresso();
System.out.println(beverage.getDescription()
+ " $" + beverage.cost());
Beverage beverage2 = new DarkRoast();
beverage2 = new Mocha(beverage2);
beverage2 = new Mocha(beverage2);
beverage2 = new Whip(beverage2);
System.out.println(beverage2.getDescription()
+ " $" + beverage2.cost());
}
}